An attempt to provide understandable and up-to-date information regarding intelligence testing, intelligence theories, personal competence, adaptive behavior and intellectual disability (mental retardation) as they relate to death penalty (capital punishment) issues. A particular focus will be on psychological measurement, statistical and psychometric issues.
Monday, December 18, 2017
Atkins court decision: Farad Roland v USA (NJ; 2018)
Friday, December 15, 2017
Does the rot start at the top? New different Flynn effect research
Does the rot start at the top?
From Twitter, a Flipboard magazine by James Thompson
As readers of this blog will know, it is usually Woodley of Menie who darkens these pages with talk of genetic ruin, while James Flynn is the plucky New Zealander…
Read it on Flipboard
Read it on unz.com
Saturday, December 9, 2017
Research review of efficacy of effort testing with culturally, ethnically, and linguistically diverse populations
Alicia Nijdam-Jones and Barry Rosenfeld Fordham University
The cross-cultural validity of feigning instruments and cut-scores is a critical concern for forensic mental health clinicians. This systematic review evaluated feigning classification accuracy and effect sizes across instruments and languages by summarizing 45 published peer-reviewed articles and unpublished doctoral dissertations conducted in Europe, Asia, and North America using linguistically, ethnically, and culturally diverse samples. The most common psychiatric symptom measures used with linguistically, ethnically, and culturally diverse samples included the Structured Inventory of Malingered Symptom-atology, the Miller Forensic Assessment of Symptoms Test, and the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI). The most frequently studied cognitive effort measures included the Word Recogni-tion Test, the Test of Memory Malingering, and the Rey 15-item Memory test. The classification accuracy of these measures is compared and the implications of this research literature are discussed.
Public Significance Statement This study suggests that there is only a modest amount of research examining the use of feigning assessment measures with linguistically, ethnically, and culturally diverse populations. As psychol-ogists in the United States and other Western, English-speaking countries assess individuals from diverse linguistic, ethnic, and cultural backgrounds, it is important that the assessment techniques that they rely on have demonstrated utility in non-English cultures and languages.
Lick on image to enlarge. Article link.

- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Research Byte: The Role of Visuospatial Ability in the Raven's Progressive Matrices
The Role of Visuospatial Ability in the Raven's Progressive Matrices
Nicolette A. Waschl, Ted Nettelbeck, and Nicholas R. Burns
School of Psychology, University of Adelaide, SA, Australia
Abstract:
Debate surrounding the role of visuospatial ability in performance on the Raven's Progressive Matrices (RPM) has existed since their conception. This issue has yet to be adequately resolved, and may have implications regarding sex differences in scores. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between RPM performance, visuospatial ability and fluid ability, and any sex differences in these relationships. Data were obtained from three samples: two University samples completed the Advanced RPM and one population-based sample of men completed the Standard RPM. All samples additionally completed an alternative measure of fluid ability, and one or more measures of visuospatial ability. Structural equation modeling was used to examine the relationships between performance on the visuospatial and fluid ability tests and performance on the RPM. Visuospatial ability was found to significantly contribute to performance on the RPM, over and above fluid ability, supporting the contention that visuospatial ability is involved in RPM performance. No sex differences were found in this relationship, although sex differences in visuospatial ability may explain sex differences in RPM scores.
Keywords: Raven's Progressive Matrices, fluid ability, visuospatial ability, sex differences
Click on images to enlarge. Article link.


- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Tuesday, November 14, 2017
Intellectual Disability and the Death Penalty: Current Issues and Controversies: Marc J. Tassé Ph.D., John H. Blume JD MAR: 9781440840142: Amazon.com: Books
Providing key information for students or professionals in the fields of criminology, education, psychology, law, and law enforcement, this book documents the legal and clinical aspects of the issues related to intellectual disability and the death penalty.
• Provides a comprehensive review of the legal and clinical aspects of the death penalty and intellectual disability
• Offers a detailed discussion of the Supreme court decision in Atkins v. Virginia as well as a review of court decisions since that 2002 ruling
• Details the diagnostic issues related to determination of intellectual disability, such as the assessment of intellectual functioning, adaptive behavior, and age of onset
• Shares best practices in clinical assessment and important forensic matters that must be considered
Thursday, November 9, 2017
Research Byte: What Causes the Anti-Flynn Effect? A Data Synthesis and Analysis of Predictors

Woodley of Menie, M. A., Peñaherrera-Aguirre, M., Fernandes, H. B. F., & Figueredo, A.-J. (2017). What Causes the Anti-Flynn Effect? A Data Synthesis and Analysis of Predictors. Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences. Advance online publication.
Article link.
Abstract
Anti-Flynn effects (i.e., secular declines in IQ) have been noted in a few countries. Much speculation exists about the causes of these trends; however, little progress has been made toward comprehensively testing these. A synthetic literature search yielded a total of 66 observations of secular IQ decline from 13 countries, with a combined sample size of 302,234 and study midyears spanning 87 years, from 1920.5 to 2007.5. Multilevel modeling (MLM) was used to examine the effect of study midyear, and (after controlling for this and other factors) hierarchical general linear modeling (GLM) was used to examine the following sequence of predictors: domain “g-ness” (a rank-order measure of g saturation) Index of Biological State (IBS; a measure of relaxed/reversed selection operating on g), per capita immigration, and the 2-way interactions IBS × g-ness and Immigration × g-ness. The MLM revealed that the anti-Flynn effect has strengthened in more recent years. Net of this, the GLM found that g-ness was a positive predictor; that is, less aggregately g-loaded measures exhibited bigger IQ declines; IBS was not a significant predictor; however immigration predicted the decline, indicating that high levels of immigration promote the anti-Flynn effect. Among the interactions there was a negative effect of the Immigration × g-ness interaction, indicating that immigration promotes IQ decline the most when the measure is higher in g-ness. The model accounted for 37.1% of the variance among the observations. (PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2017 APA, all rights reserved)
- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Tuesday, November 7, 2017
The SCOTUS Lineup on the Death Penalty
----
The SCOTUS Lineup on the Death Penalty
// Crime and Consequences Blog
The Supreme Court today announced a unanimous per curiam opinion in Dunn v. Madison. I'll repeat the Heritage Foundation's summary of the case:
[T]he Court reversed a decision of the Eleventh Circuit in an Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act (AEDPA) case. AEDPA provides that a state prisoner is entitled to federal habeas relief only if the state trial court's adjudication of the prisoner's claim "was contrary to, or involved an unreasonable application of, clearly established Federal law." In this case, an Alabama trial court sentenced Vernon Madison to death for murdering a police officer. Awaiting execution, Madison suffered several strokes and petitioned for habeas, asserting that he had become incompetent to be executed. Experts testified that although Madison could not remember the "sequence of events from the offense to his arrest to the trial or any of those details," he did understand he was "tried and imprisoned for murder and that Alabama will put him to death as punishment for that crime." The district court denied Madison's petition but the Eleventh Circuit reversed. Today, the Supreme Court reversed, holding that no Supreme Court precedent has "'clearly established' that a prisoner is incompetent to be executed because of a failure to remember his commission of the crime, as distinct from a failure to rationally comprehend the concepts of crime and punishment as applied in his case."Ginsburg, joined by Breyer and Sotomayor concurred, writing that while AEDPA precludes consideration of the question in this case, the question of "whether a State may administer the death penalty to a person whose disability leaves him without memory of him commission of a capital offense" "warrant[s] full airing." Breyer also concurred, writing separately to (once again) call into question the "unconscionably long periods of time that prisoners often spend on death row awaiting execution."
----
Read in my feedly
Sunday, October 29, 2017
Meta-analysis supports cognitive ability differentiation hypotheses (SLODOR)
The cognitive ability differentiation hypothesis, which is also termed Spearman's Law of Diminishing Returns, proposes that cognitive ability tests are less correlated and less g loaded in higher ability populations. In ad-dition, the age differentiation hypothesis proposes that the structure of cognitive ability varies across respondent age. To clarify the literature regarding these expectations, 106 articles containing 408 studies, which were published over a 100-year time span, were analyzed to evaluate the empirical basis for ability as well as age differentiation hypotheses. Meta-analyses provide support for both hypotheses and related expectations. Results demonstrate that the mean correlation and g loadings of cognitive ability tests decrease with increasing ability, yet increase with respondent age. Moreover, these effects have been nearly constant throughout the century of analyzed data. These results are important because we cannot assume an invariant cognitive structure for dif-ferent ability and age levels. Implications for practice as well as drawbacks are further discussed.

Thursday, October 26, 2017
Federal Court Rules to Protect the Interest of Incompetent North Carolina Death-Row Exoneree
----
Federal Court Rules to Protect the Interest of Incompetent North Carolina Death-Row Exoneree
// Death Penalty Information Center
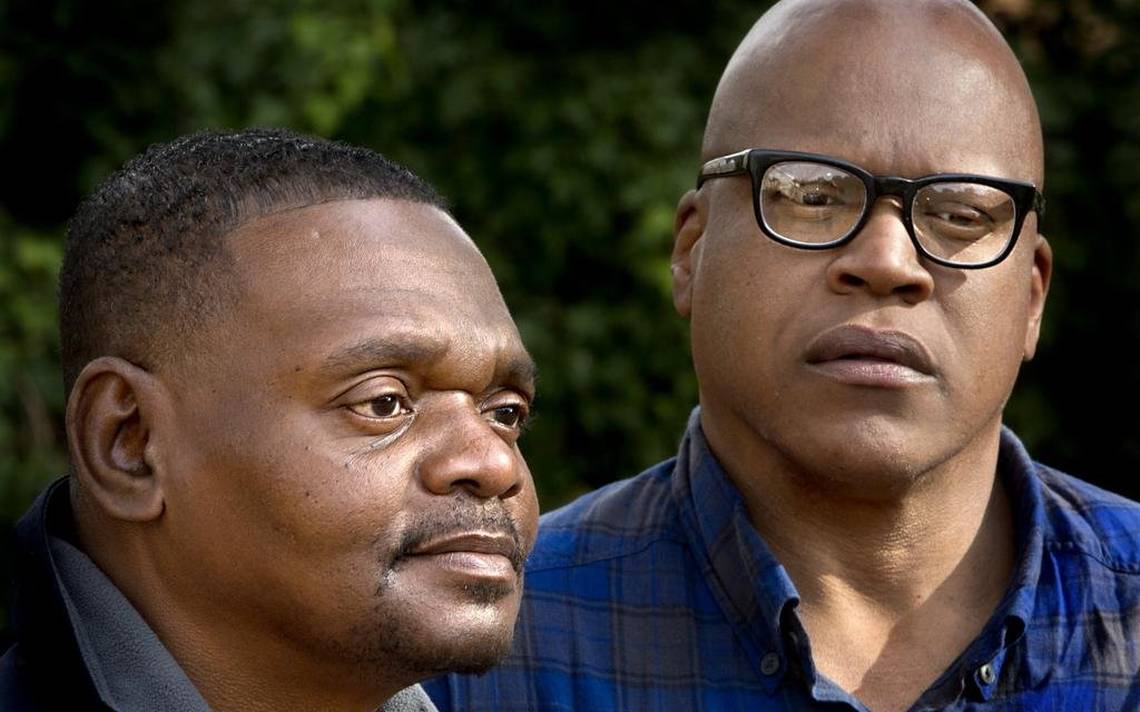 A federal judge has voided a contract that had provided Orlando-based attorney Patrick Megaro hundreds of thousands of dollars of compensation at the expense of Henry McCollum (pictured left, with his brother Leon Brown), an intellectually disabled former death-row prisoner who was exonerated in 2014 after DNA testing by the North Carolina Innocence Inquiry Commission showed that he had not committed the brutal rape and murder of a young girl for which he had been wrongly convicted and condemned. McCollum and Brown—who both have IQs measured in the 50s and 60s—had been convicted in 1983 based on coerced false confessions that the brothers (aged 19 and 15 at the time) provided to interrogating officers. At the time of his exoneration, McCollum had spent 30 years on death row and was the state's longest serving death-row prisoner. Megaro became McCollum's and Brown's lawyer in March 2015, after two women who claimed to be advocating on behalf of the brothers persuaded them to fire the lawyers who had been representing them in their efforts to obtain compensation and to hire Megaro's firm. McCollum was awarded $750,000 in compensation from North Carolina in October 2015, at least half of which appears to have been paid to Megaro. Within seven months, McCollum was out of money and taking out high-interest loans that had been arranged and approved by Megaro. Megaro also negotiated a proposed settlement of the brothers' wrongful prosecution lawsuit in which he was to receive $400,000 of a $1 million payment to the brothers. Defense lawyer Ken Rose, who represented McCollum for 20 years and helped win McCollum's release from prison, provided testimony that two mental experts had previously found that McCollum was "not competent to provide a confession" and that McCollum remained "vulnerable to manipulation and control by others." After hearing additional evidence from experts and other witnesses, U.S. District Court Judge Terrence Boyle determined that, as a result of his intellectual disability, McCollum lacked knowledge and understanding of financial issues, "remains easily manipulated," and was "unable to make important decisions about his person and property." As a result, the court voided the contract between McCollum and Megano, including the fee arrangements. Raymond Tarlton, whom Judge Boyle appointed to serve as McCollum's guardian ad litem, said the decision "made clear that the same disabilities that led to Henry McCollum giving a false confession in 1983 made him vulnerable to be manipulated and controlled after release." The court also has appointed a guardian to protect the interests of Leon Brown. Judge Boyle ordered further briefing pending receipt of the guardian's report to assist in determining the status of the contract between Megaro and Brown.
A federal judge has voided a contract that had provided Orlando-based attorney Patrick Megaro hundreds of thousands of dollars of compensation at the expense of Henry McCollum (pictured left, with his brother Leon Brown), an intellectually disabled former death-row prisoner who was exonerated in 2014 after DNA testing by the North Carolina Innocence Inquiry Commission showed that he had not committed the brutal rape and murder of a young girl for which he had been wrongly convicted and condemned. McCollum and Brown—who both have IQs measured in the 50s and 60s—had been convicted in 1983 based on coerced false confessions that the brothers (aged 19 and 15 at the time) provided to interrogating officers. At the time of his exoneration, McCollum had spent 30 years on death row and was the state's longest serving death-row prisoner. Megaro became McCollum's and Brown's lawyer in March 2015, after two women who claimed to be advocating on behalf of the brothers persuaded them to fire the lawyers who had been representing them in their efforts to obtain compensation and to hire Megaro's firm. McCollum was awarded $750,000 in compensation from North Carolina in October 2015, at least half of which appears to have been paid to Megaro. Within seven months, McCollum was out of money and taking out high-interest loans that had been arranged and approved by Megaro. Megaro also negotiated a proposed settlement of the brothers' wrongful prosecution lawsuit in which he was to receive $400,000 of a $1 million payment to the brothers. Defense lawyer Ken Rose, who represented McCollum for 20 years and helped win McCollum's release from prison, provided testimony that two mental experts had previously found that McCollum was "not competent to provide a confession" and that McCollum remained "vulnerable to manipulation and control by others." After hearing additional evidence from experts and other witnesses, U.S. District Court Judge Terrence Boyle determined that, as a result of his intellectual disability, McCollum lacked knowledge and understanding of financial issues, "remains easily manipulated," and was "unable to make important decisions about his person and property." As a result, the court voided the contract between McCollum and Megano, including the fee arrangements. Raymond Tarlton, whom Judge Boyle appointed to serve as McCollum's guardian ad litem, said the decision "made clear that the same disabilities that led to Henry McCollum giving a false confession in 1983 made him vulnerable to be manipulated and controlled after release." The court also has appointed a guardian to protect the interests of Leon Brown. Judge Boyle ordered further briefing pending receipt of the guardian's report to assist in determining the status of the contract between Megaro and Brown.(Judge nixes high attorney fees for NC man wrongly sentenced to death, Associated Press, October 24, 2017; J. Neff, Innocent, Disabled and Vulnerable, The Marshall Project, October 24, 2017; Editorial: Judge finally rules to benefit of half-brothers, The Robesonian, October 24, 2017.) Read the court's order. See Innocence and Intellectual Disability.
- 339 reads
----
Read in my feedly
Wednesday, October 25, 2017
CFA of WISC-V: A five factor CHC battery
The five factors look like clear Gc, Gv, Gf, Gwm and Gs CHC factors.
Abstract
The purpose of this research was to test the consistency in measurement of Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Chil-dren-Fifth Edition (WISC-V; Wechsler, 2014) constructs across the 6 through 16 age span and to understand the constructs measured by the WISC-V. First-order, higher-order, and bifactor confirmatory factor models were used. Results were compared with two recent studies using higher-order and bifactor exploratory factor analysis (Canivez, Watkins, & Dombrowski, 2015; Dombrowski, Canivez, Watkins, & Beaujean, 2015) and two using con-firmatory factor analysis (Canivez, Watkins, & Dombrowski, 2016; Chen, Zhang, Raiford, Zhu, & Weiss, 2015). We found evidence of age-invariance for the constructs measured by the WISC-V. Further, both g and five distinct broad abilities (Verbal Comprehension, Visual Spatial Ability, Fluid Reasoning, Working Memory, and Processing Speed) were needed to explain the covariances among WISC-V subtests, although Fluid Reasoning was nearly equivalent to g. These findings were consistent whether a higher-order or a bifactor hierarchical model was used, but they were somewhat inconsistent with factor analyses from the prior studies. We found a correlation between Fluid Reasoning and Visual Spatial factors beyond a general factor (g) and that Arithmetic was primarily a direct indicator of g. Composite scores from the WISC-V correlated well with their corresponding underlying factors. For those concerned about the fewer numbers of subtests in the Full Scale IQ, the model implied relation between g and the FSIQ was very strong.
Click on images to enlarge.



- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Monday, October 23, 2017
SCOTUS orders Florida to reconsider Atkins case in light of Moore v Texas: Tavares Wright
The United States Supreme Court has ordered the Florida Supreme Court to reconsider a decision that had denied a death-row prisoner's claim that he was ineligible for the death penalty because he has Intellectual Disability. On October 16, the Court reversed and remanded the case of Tavares Wright (pictured, left), directing the Florida courts to reconsider his intellectual-disability claim in light of the constitutional standard the Court set forth in its March 2017 decision in Moore v. Texas.
More information can be found here.
Monday, October 9, 2017
"Neuroscience Nuance: Dissecting the Relevance of Neuroscience in Adjudicating Criminal Culpability"
----
"Neuroscience Nuance: Dissecting the Relevance of Neuroscience in Adjudicating Criminal Culpability"
// Sentencing Law and Policy
The title of this post is the title of this notable new paper authored by Christopher Slobogin. Even more than the title, the paper's abstract suggests it is a must-read for sentencing fans:
Most scholars who have written about the role of neuroscience in determining criminal liability and punishment take a stance somewhere between those who assert that neuroscience has virtually nothing to say about such determinations and those that claim it will upend the assumption that most choices to commit crime are blameworthy. At the same time, those who take this intermediate position have seldom clarified how they think neuroscience can help. This article tries to answer that question more precisely than most works in this vein. It identifies five types of neuroscience evidence that might be presented by the defense and discusses when that evidence is material under accepted legal doctrine. It concludes that, even on the assumption that the data presented are accurate, much commonly proffered neuroscientific evidence is immaterial or only weakly material, not only at trial but also at sentencing. At the same time, it recognizes that certain types of neuroscience evidence can be very useful in criminal adjudication, especially at sentencing.
----
Read in my feedly
Sunday, October 1, 2017
Atkins-related Court decision: Cathey v Davis (2017, Texas)

For some reason I failed to post the most recent court decision this past May regarding Cathey, a case where the Flynn effect (norm obsolescence) is prominent. This decision can now be found here. The court granted Cathey a district court hearing to present evidence regarding the Flynn effect in his Atkins claim. Prior Cathey related posts can be found here.
- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Monday, September 25, 2017
Atkins related case: Wesely Coonce v USA Appellants Opening Brief
The opening appellant brief for the Atkin's related case of Wesley Coonce (Coonce v USA, 2016) is now available for viewing here.
Law Review Article (Meyer, 2017): The newly informed decency of death: Hall v Florida endorses the Marsshall hypothesis in eighth ammendment review of the death penalty
The above titled law review article (Meyer, 2017: The newly informed decency of death: Hall v Florida endorses the Marshall hypothesis in eighth amendment review of the death penalty can be found here.
Flynn effect reference project
I had previously maintained a "Flynn effect archive" project at this blog. In its prior form, it included a reference list and hyperlinks to almost all articles. I have now found it necessary to remove all posts (and index tag terms) related to that project. It's purpose has changed.
Originally the idea was to make available most the available research on the Flynn effect. Over time I noticed (via the hit counter tracker) that fewer and fewer people were consulting it to obtain copies of articles. The time necessary to maintain the archive, especially after I switched domain servers (which resulted in a ton of obsolete and broken hyperlinks), was not cost-effective. Thus, that archive is no longer available.
In its place I am now maintaining (and will update periodically) a simple working list of Flynn effect (aka, norm obsolescence) references. The current version, dated 09-17-17, can be downloaded by clicking here. It includes
The reference list should not be considered exhaustive of all possible published and unpublished research regarding the Flynn effect. It is the best I can put together. Any readers who locate missing articles, or new publications, should contact me via email (go to the MindHub and contact me via the contact info). I will then add those to the next update.
Enjoy.
Thursday, September 7, 2017
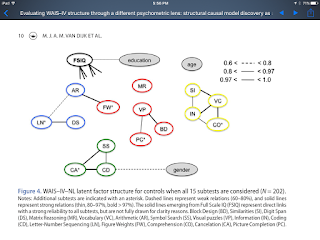
Evaluating WAIS–IV structure through a different psychometric lens: structural causal model discovery as an alternative to confirmatory factor analysis via BrowZine
van Dijk, Marjolein J. A. M.; Claassen, Tom; Suwartono, Christiany; van der Veld, William M.; van der Heijden, Paul T.; Hendriks, Marc P. H.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Vol. 31 Issue 6-7 – 2017: 1141 - 1154
10.1080/13854046.2017.1352029
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1352029
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1352029
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Sharing The use of neuropsychological tests to assess intelligence via BrowZine
Gansler, David A.; Varvaris, Mark; Schretlen, David J.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Vol. 31 Issue 6-7 – 2017: 1073 - 1086
10.1080/13854046.2017.1322149
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1322149
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1322149
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Sharing Psychometrics and statistics: two pillars of neuropsychological practice via BrowZine
Hilsabeck, Robin C.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Vol. 31 Issue 6-7 – 2017: 995 - 999
10.1080/13854046.2017.1350752
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1350752
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1350752
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Saturday, August 26, 2017
The Intelligent Brain: One of the Great Courses on sale
The Intelligent Brain
1 What Is Intelligence? Probe the nature of intelligence by looking first at the phenomenon of savants—individuals who excel at a narrow mental skill. Does this qualify as…
Read it on Flipboard
Read it on thegreatcourses.com
Friday, August 25, 2017
Validation of the Advanced Clinical Solutions Word Choice Test (WCT) in a Mixed Clinical Sample: Establishing Classification Accuracy, Sensitivity/Specificity, and Cutoff Scores via BrowZine
Validation of the Advanced Clinical Solutions Word Choice Test (WCT) in a Mixed Clinical Sample: Establishing Classification Accuracy, Sensitivity/Specificity, and Cutoff Scores
Bain, Kathleen M.; Soble, Jason R.
Assessment: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1073191117725172
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1073191117725172
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Thursday, August 10, 2017
Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals rules against Flynn effect adjustment of IQ scores in Atkins death penalty cases: Black v Carpenter (2017)
I have no further comment at this time as my expert opinion is clearly articulated in the AAIDD publication and I will continue my efforts to educate the courts. This decision is at variance with the official positions of American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities (AAIDD) and the American Psychiatric Association (DSM-5), the two professional associations with official guidance regarding the diagnosis of ID.
This looks like another issue that might need the attention of SCOTUS.
The following section is extracted from the complete ruling.
E. Implications of the Flynn Effect
There is good reason to have pause before retroactively adjusting IQ scores downward to offset the Flynn Effect. As we noted above, see n.1, supra, the Flynn Effect describes the apparent rise in IQ scores generated by a given IQ test as time elapses from the date of that specific test’s standardization. The reported increase is an average of approximately three points per decade, meaning that for an IQ test normed in 1995, an individual who took that test in 1995 and scored 100 would be expected to score 103 on that same test if taken in 2005, and would be expected to score 106 on that same test in 2015. This does not imply that the individual is “gaining intelligence”: after all, if the same individual, in 2015, took an IQ test that was normed in 2015, we would expect him to score 100, and we would consider him to be of the same “average” intelligence that he demonstrated when he scored 100 on the 1995-normed test in 1995. Rather, the Flynn Effect implies that the longer a test has been on the market after initially being normed, the higher (on average) an individual should perform, as compared with how that individual would perform on a more recently normed IQ test.
At first glance, of course, the Flynn Effect is troubling: if scoring 70 on an IQ test in 1995 would have been sufficient to avoid execution, then why shouldn’t a score of 76 on that same test administered in 2015 (which would produce a “Flynn-adjusted” score of 70) likewise suffice to avoid execution? Further, even if IQ tests were routinely restandardized every year or two to reset the mean score to 100, and even if old IQ tests were taken off the market so as to avoid the Flynn Effect “inflation” of scores that is visible when an IQ test continues to be administered long after its initial standardization, that would only mask, but not change, the fact that IQ scores are said to be rising.
Indeed, perhaps the most puzzling aspect of the Flynn Effect is that it is true. As Dr. Tassé states in his declaration, “[t]he so-called ‘Flynn Effect’ is NOT a theory. It is a wellestablished scientific fact that the US population is gaining an average of 3 full-scale IQ points per decade.” The implications of the Flynn Effect over a longer period of time are jarring: consider a cohort of individuals who, in 1917, took an IQ test that was normed in 1917 and received “normal” scores (say, 100, on average). If we could transport that same cohort of individuals to the present day, we would expect their average score today on an IQ test normed in 2017—a century later—to be thirty points lower: 70, making them mentally retarded, on average.
Alternatively, consider a cohort of individuals who, in 2017, took an IQ test that was normed in 2017 and received “normal” scores (of 100, on average). If we could transport that same cohort of individuals to a century ago, we would expect that their average score on a test normed in 1917 would be thirty points higher: 130, making them geniuses, on average.
It thus makes little sense to use Flynn-adjusted IQ scores to determine whether a criminal is sufficiently intellectually disabled to be exempt from the death penalty. After all, if Atkins stands for the proposition that someone with an IQ score of 70 or lower in 2002 (when Atkins was decided) is exempt from the death penalty, then the use of Flynn-adjusted IQ scores would conceivably lead to the conclusion that, within the next few decades, almost no one with borderline or merely below-average IQ scores should be executed, because their scores when adjusted downward to 2002 levels would be below 70. Indeed, the Supreme Court did not amplify just what moral or medical theory led to the highly general language that it used in Atkins when it prohibited the imposition of a death sentence for criminals who are “so impaired as to fall within the range of mentally retarded offenders about whom there is a national consensus,” 536 U.S. at 317. If Atkins had been a 1917 case, the majority of the population now living—if we were to apply downward adjustments to their IQ scores to offset the Flynn Effect from 1917 until now—would be too mentally retarded to be executed; and until the Supreme Court tells us that it is committed to making such downward adjustments, we decline to do so.
* * *
COLE, Chief Judge, concurring in the opinion except for Section II.E. I concur with the majority opinion except as to the section discussing the implications of the Flynn Effect. In holding that Black did not prove that he had significantly subaverage general intellectual functioning, we concluded that Black’s childhood IQ scores would be above 70 even if we adjusted those scores to account for both the SEM and the Flynn Effect. Accordingly, I would not address the question of whether we should apply a Flynn Effect adjustment in cases generally because it is unnecessary to the resolution of Black’s appeal. Regardless, courts, including our own in Black I, have regarded the Flynn Effect as an important consideration in determining who qualifies as intellectually disabled. See, e.g., Black v. Bell, 664 F.3d 81, 95–96 (6th Cir. 2011); Walker v. True, 399 F.3d 315, 322–23 (4th Cir. 2005).
Sunday, August 6, 2017
Sharing The Flynn effect for verbal and visuospatial short-term and working memory: A cross-temporal meta-analysis via BrowZine
Wongupparaj, Peera; Wongupparaj, Rangsirat; Kumari, Veena; Morris, Robin G.
Intelligence: Vol. 64 – 2017: 71 - 80
10.1016/j.intell.2017.07.006
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289616300988
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289616300988
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Thursday, July 27, 2017
APA Handbook of Forensic Neuropsychology
APA Handbook of Forensic Neuropsychology
List Price: $199.00 Member/Affiliate Price: $129.00 Quantity: FREE SHIPPING For individuals in the U.S. & U.S. territories Pages: 528 Item #: 4311532 ISBN:…
Read it on Flipboard
Read it on apa.org
Tuesday, July 25, 2017
Time processing in children with mathematical difficulties via BrowZine
Cester, Ilaria; Mioni, Giovanna; Cornoldi, Cesare
Learning and Individual Differences: Vol. 58 – 2017: 22 - 30
10.1016/j.lindif.2017.07.005
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1041608017301280
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1041608017301280
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Saturday, July 22, 2017
Evaluating WAIS–IV structure through a different psychometric lens: structural causal model discovery as an alternative to confirmatory factor analysis via BrowZine
van Dijk, Marjolein J. A. M.; Claassen, Tom; Suwartono, Christiany; van der Veld, William M.; van der Heijden, Paul T.; Hendriks, Marc P. H.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/144497457/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1352029
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Wednesday, July 19, 2017
Disconnected lives: Women with intellectual disabilities in conflict with the law via BrowZine
Levine, Kathryn Ann; Proulx, Jocelyn; Schwartz, Karen
Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/142756581/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jar.12387/pdf
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, July 18, 2017
Science, Technology, Society, and Law via BrowZine
Cole, Simon A.; Bertenthal, Alyse
Annual Review of Law and Social Science: Vol. 13 Issue 1 – 2017:
10.1146/annurev-lawsocsci-110316-113550
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-lawsocsci-110316-113550
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-lawsocsci-110316-113550
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Saturday, July 1, 2017
"Intelligent" intelligence testing with Wechsler Arithmetic test
The authors conclude "In summary, while Arithmetic may be considered a measure of concentration or working memory, it should be kept in mind that many other factors influence it and that its specificity as a concentration measure is limited."


- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Wednesday, June 28, 2017
The Diagnosis of Mental Disorders Is Influenced by Automatic Causal Reasoning via BrowZine
Flores, Amanda; Cobos, Pedro L.; Hagmayer, York
Clinical Psychological Science: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/109590019/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2167702617709560
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, June 20, 2017
Monday, June 19, 2017
Coping, Emotion Regulation, and Psychopathology in Childhood and Adolescence: A Meta-Analysis and Narrative Review. via BrowZine
Compas, Bruce E.; Jaser, Sarah S.; Bettis, Alexandra H.; Watson, Kelly H.; Gruhn, Meredith A.; Dunbar, Jennifer P.; Williams, Ellen; Thigpen, Jennifer C.
Psychological Bulletin: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/107457505/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/bul0000110
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
**
Emotion and the Prefrontal Cortex: An Integrative Review. via BrowZine
Dixon, Matthew L.; Thiruchselvam, Ravi; Todd, Rebecca; Christoff, Kalina
Psychological Bulletin: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/107457508/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/bul0000096
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Sunday, June 11, 2017
Field reliability of competency and sanity opinions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. via BrowZine
Guarnera, Lucy A.; Murrie, Daniel C.
Psychological Assessment: Vol. 29 Issue 6 – 2017: 795 - 818
10.1037/pas0000388
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000388
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000388
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Taking forensic mental health assessment “out of the lab” and into “the real world”: Introduction to the special issue on the field utility of forensic assessment instruments and procedures. via BrowZine
Edens, John F.; Boccaccini, Marcus T.
Psychological Assessment: Vol. 29 Issue 6 – 2017: 599 - 610
10.1037/pas0000475
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000475
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000475
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, May 30, 2017
Invalid before impaired: an emerging paradox of embedded validity indicators via BrowZine
Invalid before impaired: an emerging paradox of embedded validity indicators
Erdodi, Laszlo A.; Lichtenstein, Jonathan D.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/104029700/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1323119
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Thursday, May 11, 2017
False confessions via BrowZine
Kassin, Saul M.
Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://api.thirdiron.com/v2/libraries/56/articles/100524171/content
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/wcs.1439/pdf
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, May 9, 2017
Preserved cognitive functions with age are determined by domain-dependent shifts in network responsivity

Preserved cognitive functions with age are determined by domain-dependent shifts in network responsivity
Altmetric: 28 More detail Article | Open Dávid Samu • , Karen L. Campbell • , Kamen A.…
Read it on Flipboard
Read it on nature.com
Wednesday, May 3, 2017
Monday, April 24, 2017
Sharing The reliability of multidimensional neuropsychological measures: from alpha to omega via BrowZine
Watkins, Marley W.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1317364
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1317364
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Sharing Evaluation of multidimensional models of WAIS-IV subtest performance via BrowZine
McFarland, Dennis J.
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1320426
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2017.1320426
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Saturday, April 1, 2017
Sharing A Negative Flynn Effect in Kuwait: The same effect as in Europe but with seemingly different causes via BrowZine
Dutton, Edward; Bakhiet, Salaheldin Farah; Essa, Yossry Ahmed Sayed; Blahmar, Tahanei Abdulrahman Muhammad; Hakami, Sultan Mohammed Ahmed
Personality and Individual Differences: Vol. 114 – 2017: 69 - 72
10.1016/j.paid.2017.03.060
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191886917302301
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191886917302301
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, March 28, 2017
SCOTUS blog summary of Moore v Texas Atkins decision
SCOTUSblog
- Opinion analysis: A victory for intellectually disabled inmates in Texas
- Argument transcript
- Argument analysis: Justices hesitant about extending ERISA to church-affiliated pension plans
- Argument preview: Court to weigh suppression of evidence in notorious D.C. murder
- Live blog of opinions (Update: Completed)
- Tuesday round-up
- Petition of the day
- Argument transcripts
Opinion analysis: A victory for intellectually disabled inmates in Texas
Posted: 28 Mar 2017 10:51 AM PDT
A Texas death-row inmate will get a shot at a new sentence after the Supreme Court ruled today that a state court applied the wrong standards to conclude that he was not intellectually disabled and therefore could be executed. Bobby James Moore was convicted and sentenced to death for shooting a supermarket employee during a 1980 robbery. But Moore argued that he was exempt from execution because he was intellectually disabled – for example, he failed first grade twice, still did not grasp basic principles like telling time at the age of 13, and had suffered a "debilitating" injury when he was hit in the head with a chain and a brick during the battle over integrating public schools.
The Texas Court of Criminal Appeals – the state's court of last resort for criminal cases – rejected Moore's challenge to his death sentence. It relied on its 2004 decision in another case, Ex parte Briseno, involving an inmate's intellectual disability. Briseno used a set of 1992 standards for evaluating intellectual disability, along with several "evidentiary factors" that take into account, among other things, whether the people who knew the inmate best when he was growing up regarded him as intellectually disabled. Moore asked the Supreme Court to weigh in; today the justices, by a vote of 5-3, vacated the Texas court's ruling and sent the case back for a new look.
Justice Ginsburg with opinion in Moore v. Texas (Art Lien)
In an opinion by Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg that was joined by Justices Anthony Kennedy, Stephen Breyer, Sonia Sotomayor and Elena Kagan, the court acknowledged that its recent decisions on intellectual disability and the death penalty assign to the states the primary responsibility for "the task of developing appropriate ways to enforce" the Constitution's bar on executing intellectually disabled inmates. But, the court explained, those decisions do not give the states free rein: Although states do not have to follow every detail of the most recent medical guide on intellectual disabilities, they cannot disregard the standards in those guides either.
In this case, the court concluded, the Texas court's ruling was wrong in multiple respects. First, the justices reasoned, the Texas court should not have focused just on Moore's IQ score of 74. Instead, the Texas court should have also considered the standard error of measurement – that is, the amount that scores could fluctuate around a "true" score. Looked at that way, Moore's score would range from 69 to 79, which would have required the Texas court to consider other evidence of his possible intellectual disability.
The Texas court's decision was also flawed, the Supreme Court continued, because it did not consider current clinical standards when evaluating how well Moore could handle the demands of everyday life, which is a key factor in determining whether someone is intellectually disabled. For example, the Texas court emphasized Moore's strengths – such as that he "lived on the streets, mowed lawns, and played pool for money" – when clinical standards indicate that it should have focused on his deficits.
The Texas court made the problem even worse, the justices reasoned, when it looked to the "evidentiary factors" outlined in the Briseno case. Those factors were essentially invented by the Texas court, without any basis in either medicine or law; indeed, even Texas itself does not use them to determine whether someone is intellectually disabled in other contexts. Instead, the court stressed, the factors rely on inaccurate stereotypes of the intellectually disabled by laypeople and are intended to reflect a consensus by Texans as to which defendants should or should not be subject to the death penalty. But even if an inmate has a relatively mild disability, the court emphasized, such that the Briseno factors would suggest that he is not exempt from execution, the Constitution bars the states from executing anyone with an intellectual disability.
Chief Justice John Roberts dissented from today's ruling, in an opinion joined by Justices Samuel Alito and Clarence Thomas. As an initial matter, Roberts agreed with the majority that the Texas court's reliance on the Briseno evidentiary factors was "incompatible with the Eighth Amendment." But, in Roberts' view, that conclusion was irrelevant, because he would have let stand the Texas court's conclusion that, based on his IQ, Moore was not intellectually disabled. More broadly, Roberts complained that the court's ruling today does not give states enough guidance about how to proceed in similar cases going forward: "States have 'some flexibility' but cannot 'disregard' medical standards. Neither the Court's articulation of this standard nor its application sheds any light on what it means."
After the oral argument, today's decision was not entirely unexpected. But it still represents a big victory for Bobby James Moore and other intellectually disabled inmates on death row in Texas. And it will likely lead to new litigation in the other states that have not adopted legal definitions of intellectual disability that are not specifically based on the current medical standards. Whether it will lead to the confusion at which Roberts hints remains to be seen.
The post Opinion analysis: A victory for intellectually disabled inmates in Texas appeared first on SCOTUSblog.
--
Institute for Applied Psychometrics (IAP)
************************************************
Breaking News: SCOTUS vacates Moore v Texas Atkins decision: Briseno adaptive behavior standards not consistent with medical consensus

SCOTUS has vacated Moore v Texas which had as the central issue the inappropriate use of the state of Texas's unusual Briseno adaptive behavior standards.
Prior posts regarding this case can be found here. The history of the case before SCOTUS is available at the SCOTUS blog. A copy of the decision can be accessed here.
- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Sunday, March 26, 2017
"The Misjudgment of Criminal Responsibility"
----
"The Misjudgment of Criminal Responsibility"
// Neuroethics & Law Blog
Recently Published on SSRN: "The Misjudgment of Criminal Responsibility" ROBERT A. BEATTEY, CUNY, John Jay College of Criminal Justice MARK R. FONDACARO, J.D., PH.D., John Jay College - CUNY Generally, a criminal statute must consist of two essential elements: a...
----
Read in my feedly
Saturday, March 25, 2017
Sharing A Synthesis of the Effects of Correctional Education on the Academic Outcomes of Incarcerated Adults via BrowZine
Reed, Deborah K.
Educational Psychology Review: Vol. 27 Issue 3 – 2015: 537 - 558
10.1007/s10648-014-9289-8
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10648-014-9289-8
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10648-014-9289-8
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Saturday, March 11, 2017
Sharing Reducing the effect size of the retest effect: Examining different approaches via BrowZine
Arendasy, Martin E.; Sommer, Markus
Intelligence: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289616302963
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289616302963
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Wednesday, March 8, 2017
Sharing Relative Utility of Performance and Symptom Validity Tests via BrowZine
Copeland, Christopher T.; Mahoney, James J.; Block, Cady K.; Linck, John F.; Pastorek, Nicholas J.; Miller, Brian I.; Romesser, Jennifer M.; Sim, Anita H.
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology: Vol. 31 Issue 1 – 2016: 18 - 22
10.1093/arclin/acv065
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=https://academic.oup.com/acn/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/arclin/acv065
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
https://academic.oup.com/acn/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/arclin/acv065
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Sharing Stability in Test-Usage Practices of Clinical Neuropsychologists in the United States and Canada Over a 10-Year Period: A Follow-Up Survey of INS and NAN Members via BrowZine
Rabin, Laura A.; Paolillo, Emily; Barr, William B.
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology: Vol. 31 Issue 3 – 2016: 206 - 230
10.1093/arclin/acw007
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=https://academic.oup.com/acn/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/arclin/acw007
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
https://academic.oup.com/acn/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/arclin/acw007
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, March 7, 2017
Impact of Neuroscience and Evolving Standards of Decency on Juvenile Sentencing | Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law
Impact of Neuroscience and Evolving Standards of Decency on Juvenile Sentencing | Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law
Discussion This series of U.S. Supreme Court decisions has…
Read it on Flipboard
Read it on jaapl.org
Saturday, March 4, 2017
Sharing Multi-group and hierarchical confirmatory factor analysis of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Fifth Edition: What does it measure? via BrowZine
Reynolds, Matthew R.; Keith, Timothy Z.
Intelligence: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016028961630201X
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016028961630201X
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Friday, March 3, 2017
Sharing Trial 1 Versus Trial 2 of the Test of Memory Malingering: Evaluating Accuracy Without a “Gold Standard”. via BrowZine
Mossman, Douglas; Wygant, Dustin B.; Gervais, Roger O.; Hart, Kathleen J.
Psychological Assessment: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000449
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000449
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Friday, February 3, 2017
Court Decision: Another Hall v Florida related remand in Florida: Nixon v Florida (2017)

Yet another remand for an ID hearing in Florida as a result of Hall v Florida 2014 decision. This time Nixon v Florida (click here for remand order). Prior information regarding this case can be found here.
- Posted using BlogPress from my iPad
Wednesday, January 25, 2017
Research Bytes: Specificity rates for non-clinical, bilingual, Mexican Americans on three popular performance validity measures via BrowZine
Gasquoine, Philip G.; Weimer, Amy A.; Amador, Arnoldo
The Clinical Neuropsychologist: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2016.1277786
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13854046.2016.1277786
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Research Bytes: Cross-Cultural Feigning Assessment: A Systematic Review of Feigning Instruments Used With Linguistically, Ethnically, and Culturally Diverse Samples. via BrowZine
Nijdam-Jones, Alicia; Rosenfeld, Barry
Psychological Assessment: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000438
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/pas0000438
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Tuesday, January 24, 2017
Research Byte: Is ability-based emotional intelligence impervious to the Flynn effect? A cross-temporal meta-analysis (2001–2015) via BrowZine
Pietschnig, Jakob; Gittler, Georg
Intelligence: Articles in press
University of Minnesota Users:
http://login.ezproxy.lib.umn.edu/login?url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289616301908
Non-University of Minnesota Users: (Full text may not be available)
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289616301908
Accessed with BrowZine, supported by University of Minnesota.
Monday, January 23, 2017
Texas Court Orders Release of Former Death Row Prisoner Who...
|